Driving in the Netherlands by car is, for many reasons, a real great pleasure and comfort.
First – the roads are in a very good condition, although their standard depends on the category of course.
Second – the number of road signs, especially those limiting speed, has been reduced to a necessary minimum. In addition, junctions are replaced by roundabouts.
Third – Dutch drivers like to drive responsibly and respect traffic regulations.
A country with such an extensive amount of roads and one of the densiest networks in the world (139.295 km of public roads; 64 km of motorways per 1000 km) has to care much about the traffic safety.
Motorways in the Netherlands
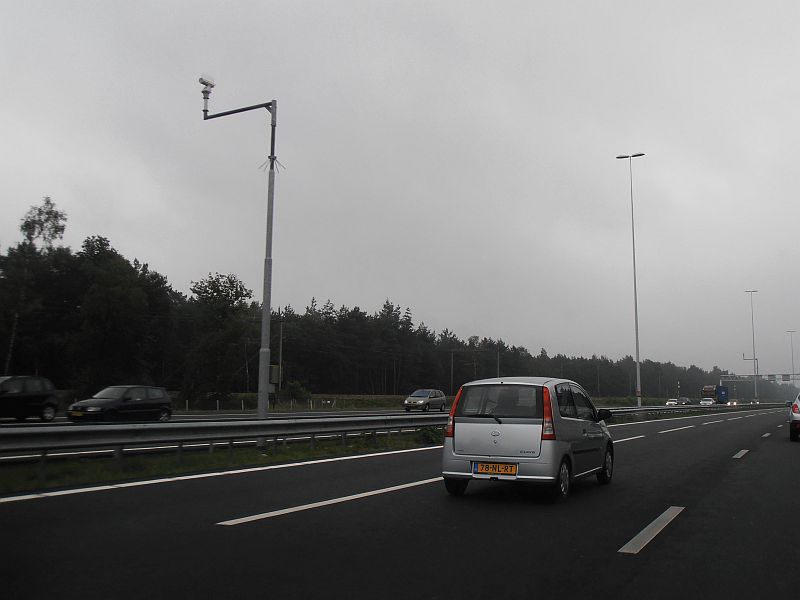
 This is why there are numerous cameras on the motorways and dual carriageways, positioned every few meters. Traffic police is practically invisible, but let one drive too fast on the highway and you can hear a police car chasing him!
This is why there are numerous cameras on the motorways and dual carriageways, positioned every few meters. Traffic police is practically invisible, but let one drive too fast on the highway and you can hear a police car chasing him!
Cameras on the motorway
Fine has to be payed and there is no exception in that. Therefore the Netherlands with a very dense population in Europe has the lowest rate of deaths in car accidents. For the year 2012 – it was 34 killed for 1 million inhabitants, while the Polish rate amounted to as much as 93 killed (source: www.niedziela.nl).
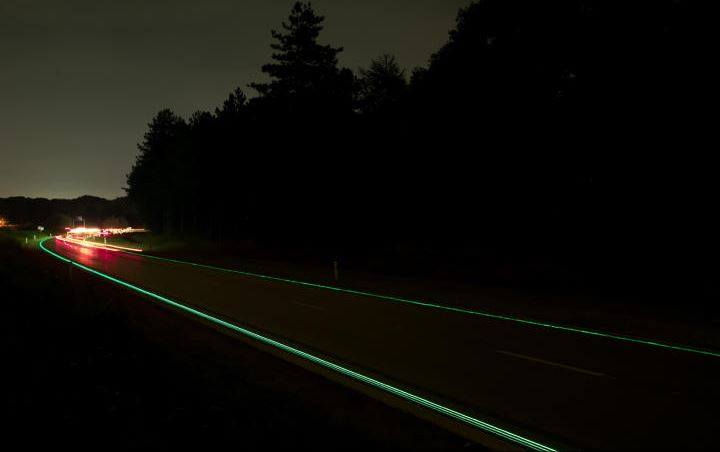
To care more about the road safety the Dutch are testing highway stripes glowing in the dark. The paint used for this purpose is luminescent. During the day it soaks the sunlight so after dark it glows slightly in green. The effect can be maintained up to eight hours. The test section is located on the N329 motorway, near the town of Oss and is about 500 meters long.
Glowing highway by Oss
Besides the time of going to and from the work in the big city areas, driving in the Netherlands is very smooth, thanks to minimalizing lights and a high density of the road network. According to the administration, roads are categorized into 4 types:
1. National roads (Rijkswegen) – most motorways and express roads. Those road numbers counting one or two digits (regardless of the preceding letter) are mostly national roads.
2. Provincial roads – they are indicated by a letter and three numbers; only a small number of provincial roads are motorways (they were in the past national roads).
Provincial road – South Holland
3. Municipality roads – they make up the bulk of the network.
4. Roads managed by water management boards (there are 24), which arises from the fact that those roads are part of the dijks and dams or provide primary access.
In terms of features and the role that they play, the Dutch roads are divided into:
Motorways (autosnelweg / snelweg ) – permitted speed = 130 km/h (if there is no limit to the 120 or 100 km/h).
 Express roads (autoweg) – usual speed limit = 100 km/h. Autowegen are always numbered and mostly signposted with an N (for Non motorway highway) and up to three digits, like N34. Almost all of these expressways are national or provincial roads.
Express roads (autoweg) – usual speed limit = 100 km/h. Autowegen are always numbered and mostly signposted with an N (for Non motorway highway) and up to three digits, like N34. Almost all of these expressways are national or provincial roads.
N roads –other Non motorway highways, that aren’t expressways either, are simpler in design, with level int ersections and mostly single carriageways. Nevertheless, many of them feature adjacent bicycle tracks. Speed limit = 80 km/h (sometimes 60 km) and farm traffic and slow road users are not allowed. Those roads are indicated by N letter and typically three digits. Primary N-roads are numbered up to N400, N-roads of secondary importance are numbered 401 through 999. Most of this type are provincial roads.
ersections and mostly single carriageways. Nevertheless, many of them feature adjacent bicycle tracks. Speed limit = 80 km/h (sometimes 60 km) and farm traffic and slow road users are not allowed. Those roads are indicated by N letter and typically three digits. Primary N-roads are numbered up to N400, N-roads of secondary importance are numbered 401 through 999. Most of this type are provincial roads.
Built-up areas
Inside of built-up areas, all roads are municipal. Speed limit = 50 km/h, and except for arterials with a dual carriageway – these may be 70 km/h.
Bicycle tracks have to run separately.
A special type of arterials are:
Stadroutes (city roads)
 they form a network of numbered arterials that connect parts of a city to a ring road or motorways running outside the city. City routes are signposted prefixed by an s and numbered from 100 or 101. Number 100 indicate an inner city ring road around the city’s centre. Stadsroutes can so far be found in five Dutch cities: in Amsterdam, in Rotterdam, in the Hague, in Almere and in Nijmegen.
they form a network of numbered arterials that connect parts of a city to a ring road or motorways running outside the city. City routes are signposted prefixed by an s and numbered from 100 or 101. Number 100 indicate an inner city ring road around the city’s centre. Stadsroutes can so far be found in five Dutch cities: in Amsterdam, in Rotterdam, in the Hague, in Almere and in Nijmegen.
Ring – inner city road of a circle form and not numbered.
 Woonerf – made for a social city life area. They may use the full width of the street to walk, talk and play. Legally, pedestrians and children have priority over all other road users. The speed limit = 15 km/h and parking is also restricted.
Woonerf – made for a social city life area. They may use the full width of the street to walk, talk and play. Legally, pedestrians and children have priority over all other road users. The speed limit = 15 km/h and parking is also restricted.
Fietsstraat – a street intended primarily for cycling. Cycling takes place over the entire width of the roadway, which is red like for the bike path. Cyclist takes precedence over the car.
In a road accident
Good signage helps the emergency services to get quickly to the scene of a traffic accident. Each motorway has every hundred meters a hectometersign with the actual data on it: the name of the province, the road number and the distance to the start of the road (in this example, 41.0 km). Along the highways these signs are, because the central partition, on both sides of the road. On these plates is therefore Li (left) or Re (right). All this information is highly desirable when calling the emergency number 112.
Photo: Renata Głuszek, Wikipedia, www.fastcodesign.com